Ancient Origins and Early Influences: The Evolution Of House Styles Over Time
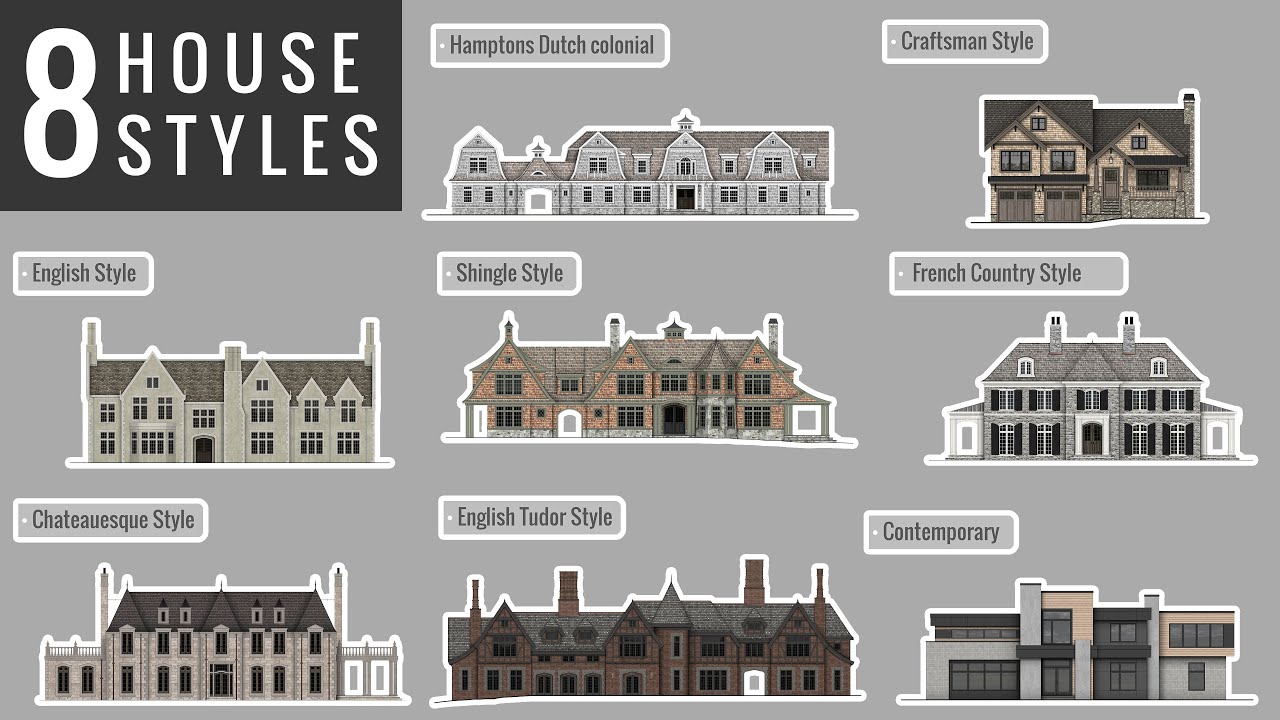
The evolution of house styles is a fascinating journey that spans millennia, reflecting the ingenuity and adaptability of humankind. From the humble beginnings of early shelters to the elaborate structures of ancient civilizations, the story of housing reveals the interplay of social, cultural, and environmental factors.
The earliest forms of human dwellings were likely simple shelters constructed from natural materials like branches, leaves, and animal skins. As humans transitioned from nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyles to settled agricultural societies, the need for more permanent and functional dwellings arose. This shift led to the development of rudimentary structures made of mud bricks, stone, and wood, which provided greater protection from the elements and served as a base for more complex social organizations.
Ancient Egyptian Housing
Ancient Egyptian housing reflects the unique societal structure and climatic conditions of the Nile Valley. The vast majority of Egyptians lived in modest mud-brick houses, often clustered together in small villages. These dwellings typically consisted of a single room with a flat roof and a small courtyard. The use of mud bricks was a practical choice, as the material was readily available and provided good insulation against the desert heat.
The wealthier classes enjoyed larger and more elaborate houses, often featuring multiple rooms, courtyards, and even gardens. These houses were often adorned with intricate carvings and paintings, reflecting the artistic sophistication of Egyptian society. The tombs of wealthy Egyptians provide valuable insights into the design and layout of their houses, showcasing the importance of family and the afterlife in their cultural beliefs.
The Rise of Modernism and Industrialization

The late 19th and early 20th centuries witnessed a profound shift in architectural thought and practice, giving rise to modernism. This movement, fueled by industrialization and technological advancements, challenged traditional architectural norms and embraced new materials, construction techniques, and design principles.
The Principles of Modernism, Functionalism, and International Style
Modernism, functionalism, and the International Style, while distinct, share a common thread: a focus on functionality, simplicity, and rationality. Modernism, a broader movement, emphasized clean lines, geometric forms, and the use of new materials like steel and glass. Functionalism, rooted in the belief that form should follow function, prioritized the practical needs of the building over decorative elements. The International Style, a more specific expression of modernism, emerged in the 1920s and promoted a universal, minimalist aesthetic, characterized by white walls, flat roofs, and large windows.
"Form follows function—that has been misunderstood. Form and function should be one, joined in a spiritual union." - Frank Lloyd Wright
Key Figures and Movements
The evolution of modern housing was shaped by influential figures and movements that championed these principles.
- Frank Lloyd Wright, an American architect, is considered a pioneer of modern architecture. His Prairie School style, characterized by horizontal lines, open floor plans, and integration with the natural environment, paved the way for modern residential design.
- Le Corbusier, a Swiss-French architect, was a leading figure in the International Style. His "Five Points of Architecture" - free facade, roof garden, pilotis (supporting columns), free plan, and long windows - became influential principles in modern housing.
- Walter Gropius, a German architect, founded the Bauhaus, a school of design that integrated art, craft, and technology. The Bauhaus emphasized functionality and simplicity, and its influence extended beyond architecture to various fields.
- Mies van der Rohe, a German architect, also associated with the Bauhaus, championed the use of steel and glass in his buildings. His "less is more" philosophy emphasized minimalism and the beauty of materials.
Contemporary Housing Trends

Contemporary housing styles reflect the changing needs and aspirations of modern society. They prioritize functionality, sustainability, and aesthetic appeal, often blending elements from various architectural traditions. This section explores the defining characteristics of contemporary house styles and examines emerging trends in sustainable and innovative housing designs.
Contemporary House Styles and Their Defining Characteristics
Contemporary house styles are characterized by their clean lines, open floor plans, and use of natural materials. They often feature large windows, high ceilings, and a focus on indoor-outdoor living. Here is a table showcasing some of the most popular contemporary house styles and their defining characteristics:
| Style | Key Features | Materials | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Modern | Minimalist design, flat roofs, geometric shapes, large windows, open floor plans | Concrete, steel, glass, wood | The Farnsworth House by Mies van der Rohe, The Case Study Houses in Los Angeles |
| Mid-Century Modern | Clean lines, geometric shapes, use of natural materials, cantilevered balconies, open floor plans | Wood, brick, stone, glass | The Eames House in Los Angeles, The Fallingwater House by Frank Lloyd Wright |
| Contemporary | Modern aesthetic with a focus on sustainability, use of natural materials, green roofs, solar panels | Wood, bamboo, recycled materials, sustainable building materials | The GreenPix Zero Energy Home in California, The Living Building Challenge homes |
| Industrial | Exposed brick, metal beams, high ceilings, open floor plans, use of reclaimed materials | Metal, brick, wood, concrete | Loft apartments in New York City, Industrial-style homes in Brooklyn |
| Mediterranean | Terracotta roofs, stucco walls, arched doorways, courtyards, use of natural materials | Stone, stucco, terracotta, wood | Homes in Southern California, Spain, and Italy |
Emerging Trends in Sustainable and Innovative Housing Designs, The evolution of house styles over time
Contemporary housing trends are increasingly focused on sustainability and innovation. Architects and designers are exploring new ways to create homes that are energy-efficient, environmentally friendly, and adaptable to changing needs. Some of the emerging trends in sustainable and innovative housing designs include:
- Net-Zero Energy Homes: These homes are designed to produce as much energy as they consume, using renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines.
- Passive House Design: This design approach focuses on minimizing energy loss through superior insulation, airtight construction, and efficient heating and cooling systems.
- Modular Homes: Modular homes are prefabricated units that are assembled on-site, offering faster construction times, lower costs, and greater flexibility in design.
- Smart Homes: Smart homes use technology to automate and control various functions, such as lighting, temperature, and security, enhancing comfort, efficiency, and safety.
- Vertical Cities: As urban populations grow, vertical cities are emerging as a solution for space constraints. These high-rise structures integrate residential, commercial, and recreational spaces, creating self-contained communities.
The Future of Housing
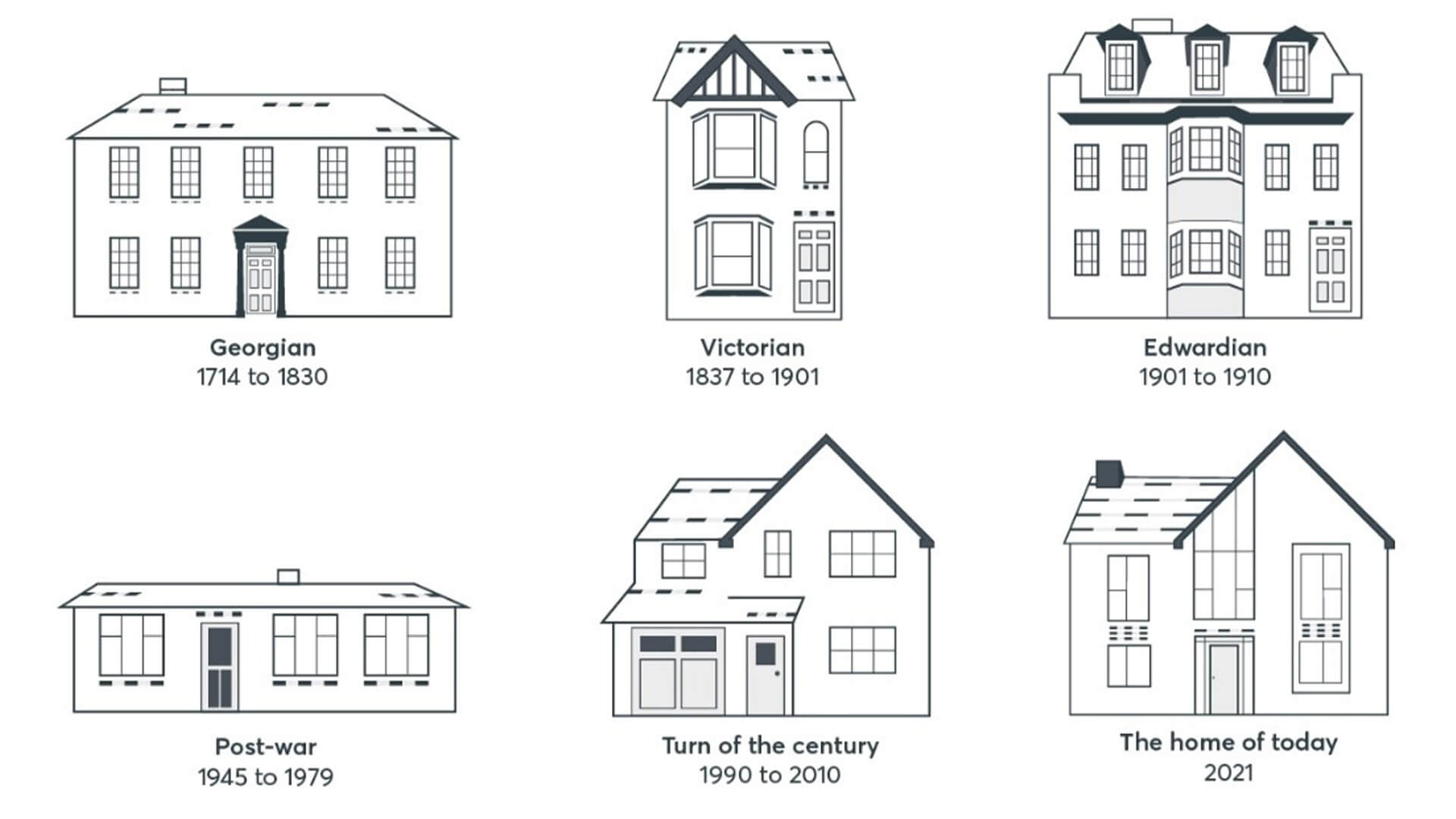
The future of housing is a dynamic landscape shaped by a confluence of technological advancements, environmental concerns, and evolving societal needs. As we navigate the 21st century, housing is poised to undergo a profound transformation, embracing innovation and sustainability to meet the challenges and opportunities of the future.
Impact of Technology
Technology is a driving force in reshaping the housing landscape, influencing design, construction, and functionality.
- Smart Homes: Homes are becoming increasingly intelligent, incorporating sensors, automation, and connectivity to enhance comfort, security, and energy efficiency. Smart home technologies allow for remote control of lighting, temperature, appliances, and security systems, creating a seamless and personalized living experience.
- 3D Printing: 3D printing is revolutionizing construction, enabling the rapid and efficient creation of custom-designed homes. This technology allows for greater flexibility in design, reduces waste, and potentially lowers construction costs. Examples include the use of 3D printing to create modular housing units or intricate architectural features.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality: Virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) are transforming the way we design, visualize, and interact with homes. VR allows potential buyers to experience virtual walkthroughs of properties, while AR can overlay digital information onto real-world environments, aiding in home design and renovation decisions.
Impact of Climate Change
Climate change presents significant challenges for the housing sector, necessitating innovative approaches to design and construction.
- Sustainable Materials: The use of sustainable materials, such as bamboo, recycled plastics, and bio-based composites, is becoming increasingly important in reducing the environmental footprint of housing. These materials offer a balance of durability, aesthetics, and environmental responsibility.
- Energy Efficiency: Energy-efficient designs, including passive solar heating, green roofs, and high-performance insulation, are crucial for reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions. Such features minimize reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to a more sustainable housing sector.
- Climate-Resilient Design: As extreme weather events become more frequent, climate-resilient design is essential for protecting homes from floods, droughts, and other climate-related hazards. This includes elevated structures, flood-resistant materials, and water-harvesting systems.
Impact of Societal Shifts
Shifting societal values and demographics are influencing housing trends.
- Urbanization: As populations continue to migrate to urban areas, there is a growing demand for compact, multi-functional housing solutions. This trend is driving the development of vertical cities, mixed-use developments, and innovative approaches to urban density.
- Aging Population: The aging population requires housing that is accessible, adaptable, and supports independent living. This includes features like universal design, smart home technologies, and community-based housing options.
- Changing Family Structures: Evolving family structures, including single-person households and blended families, are influencing housing preferences. Flexible floor plans, multi-generational homes, and co-living arrangements are emerging to cater to these diverse needs.
Futuristic Housing Concepts
Conceptual housing designs offer glimpses into the future of living.
- Vertical Cities: Vertical cities are ambitious projects that aim to maximize urban density by building upwards. These structures incorporate green spaces, sustainable technologies, and integrated infrastructure, creating self-sufficient urban environments. Examples include the proposed "City in the Sky" project in Dubai, which envisions a series of interconnected towers that can house a large population.
- Underwater Homes: As land becomes increasingly scarce, underwater homes are being explored as potential solutions. These innovative structures can be designed to withstand the pressures of the ocean and offer unique living experiences. Examples include the "Ocean Spiral" project, a proposed underwater city that would feature research facilities, residential areas, and sustainable energy sources.
- Modular Homes: Modular homes are prefabricated units that can be assembled on-site, reducing construction time and costs. These homes can be customized to suit individual needs and preferences, and can be easily adapted to changing circumstances. Examples include the "Katerra" modular housing system, which uses robotics and advanced manufacturing techniques to create high-quality, affordable homes.
FAQ Corner
The evolution of house styles over time - What are some of the most popular house styles today?
Contemporary, farmhouse, mid-century modern, craftsman, and traditional styles are among the most popular house styles today.
How has technology impacted house styles over time?
Technology has played a significant role in shaping house styles, from the introduction of new materials and construction methods to the integration of smart home technology and sustainable energy solutions.
What are some of the challenges facing future housing design?
Challenges include climate change, resource scarcity, population growth, and the need for sustainable and affordable housing solutions.
