Understanding Your Climate
Before you start planting, it's crucial to understand the specific climate conditions in your area. Plants are sensitive creatures, and their growth and well-being depend heavily on the environment they're in. This means that knowing your climate is the first step towards choosing the right plants for your garden.
Key Climate Factors
Understanding your climate involves recognizing the key factors that influence plant growth. These include:
- Temperature: Plants have specific temperature ranges they thrive in. Some prefer warm climates, while others flourish in cooler regions. Knowing the average high and low temperatures in your area will help you choose plants that can withstand the extremes.
- Sunlight: Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, the process plants use to create energy. The amount of sunlight your garden receives each day will determine which plants can thrive. Some plants need full sun, while others prefer shade.
- Rainfall: Water is crucial for plant growth. Knowing the average rainfall in your area will help you determine if you need to provide additional irrigation or choose plants that are drought-tolerant.
- Soil Type: Soil plays a vital role in providing nutrients and moisture to plants. The type of soil in your garden will influence which plants can grow successfully. Different plants have different soil preferences, some preferring sandy soil, while others need clay soil.
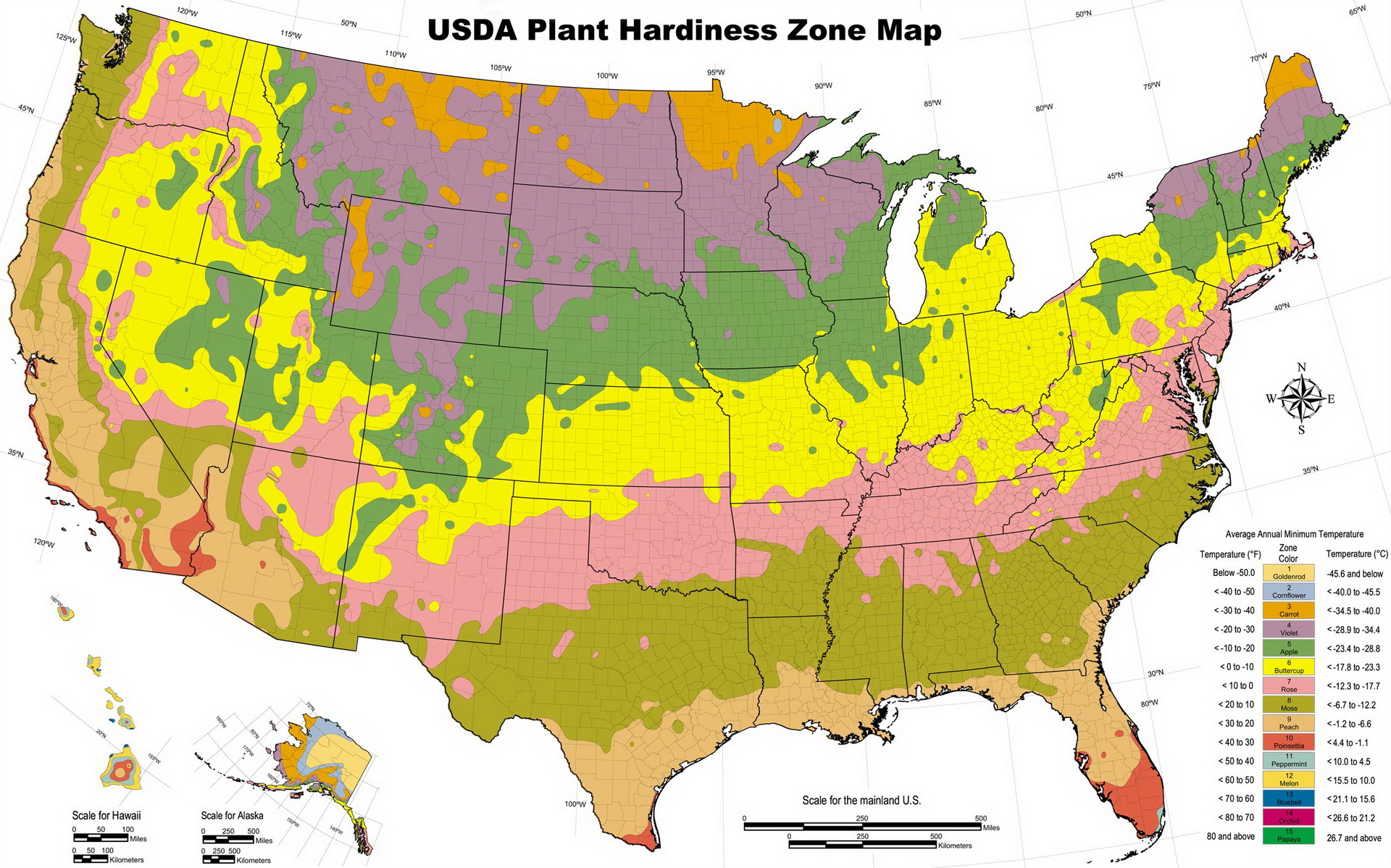
Determining Your Climate Zone
To understand your climate zone, you can use online tools or consult with local gardening experts. These resources will help you identify your specific climate zone based on your location's average temperature and rainfall. Each climate zone has specific characteristics that affect plant suitability.
Climate Zones and Plant Suitability
Once you know your climate zone, you can begin exploring the types of plants that thrive in that region. Different climate zones have different plant suitability. Here's a breakdown of some common climate zones and their respective plant preferences:
- Tropical Climates: These zones experience high temperatures and rainfall throughout the year. Tropical plants like orchids, palm trees, and banana trees thrive in these conditions.
- Subtropical Climates: These zones have warm temperatures and moderate rainfall. Citrus trees, avocado trees, and flowering shrubs like hibiscus are well-suited to subtropical climates.
- Temperate Climates: These zones have distinct seasons with moderate temperatures and rainfall. Temperate climates are ideal for a wide variety of plants, including deciduous trees, flowering perennials, and vegetables.
- Mediterranean Climates: These zones have warm, dry summers and cool, wet winters. Plants that are drought-tolerant and can withstand hot summers, such as olive trees, lavender, and rosemary, are well-suited to Mediterranean climates.
- Arid Climates: These zones have low rainfall and extreme temperatures. Plants that are drought-tolerant and can withstand hot, dry conditions, such as cacti, succulents, and desert shrubs, are best for arid climates.
Choosing the Right Plants: Choosing The Right Plants For Your Climate

Imagine a vibrant garden teeming with life, a lush oasis where flowers bloom in every shade and butterflies dance among fragrant foliage. But achieving this botanical paradise requires more than just a green thumb; it demands a deep understanding of the intricate relationship between plants and their environment. Choosing the right plants for your climate is the foundation upon which a thriving garden is built.
Selecting Plants Adapted to Your Climate
Just as humans thrive in certain climates, so too do plants. Selecting plants that are naturally suited to your region ensures they will flourish, minimizing the need for constant care and intervention. Understanding the nuances of your climate, including its temperature, humidity, and rainfall patterns, is crucial for choosing plants that will thrive.
Plant Selection Guide
This table provides a glimpse into the world of plant selection, highlighting key features and care requirements for various plant types in different climate zones:
| Plant Type | Climate Zone | Key Features | Care Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cacti and Succulents | Hot and Dry | Water-storing tissues, shallow roots, spines for protection | Minimal watering, well-drained soil, full sun |
| Drought-Tolerant Shrubs | Hot and Dry | Deep roots, leathery leaves, reduced transpiration | Occasional watering, well-drained soil, full sun |
| Deciduous Trees | Temperate | Lose leaves in fall, dormant in winter, vibrant fall foliage | Regular watering, well-drained soil, full sun to partial shade |
| Flowering Shrubs | Temperate | Produce showy flowers, various bloom times, attract pollinators | Regular watering, well-drained soil, full sun to partial shade |
| Perennial Flowers | Temperate | Return year after year, diverse colors and shapes, attract pollinators | Regular watering, well-drained soil, full sun to partial shade |
| Evergreen Trees | Cold and Wet | Maintain foliage year-round, provide shelter, dense canopy | Regular watering, well-drained soil, full sun to partial shade |
| Ferns and Mosses | Cold and Wet | Thriving in shade, moisture-loving, add texture and color | Regular watering, well-drained soil, shade |
Choosing Plants Based on Aesthetics, Growth Habits, and Maintenance Needs
Once you've narrowed down your plant choices based on climate, consider your aesthetic preferences, the space available, and your willingness to dedicate time to care.
"The beauty of a garden lies not just in its flowers, but in the harmony between the plants and their environment."
For example, if you prefer a low-maintenance garden, choose plants that are drought-tolerant and require minimal pruning. If you desire a vibrant display of color, opt for flowering shrubs or annuals that bloom throughout the growing season.
Planting and Care

Once you've chosen the right plants for your climate, it's time to get them in the ground and give them the care they need to thrive. The planting process and ongoing maintenance can vary significantly depending on your specific climate zone and the type of plants you've selected.
Optimal Planting Times
The best time to plant varies depending on your climate zone and the specific plant species. In general, it's best to plant trees and shrubs in the early spring or fall when the soil is still cool and moist. Planting during these seasons allows the roots to establish themselves before the heat of summer or the cold of winter.
For annuals and vegetables, planting times are more flexible, but it's generally best to plant them after the last frost in the spring. Check your local weather forecast or consult a gardening calendar for specific planting dates in your area.
Planting Techniques
The method of planting varies depending on the type of plant and the size of the root ball.
* Trees and Shrubs: Dig a hole twice as wide and as deep as the root ball. Gently loosen the roots and spread them out in the hole. Backfill the hole with soil, making sure to leave the root ball at or slightly above ground level. Water thoroughly after planting.
* Annuals and Vegetables: For small plants, you can simply dig a small hole and drop the plant in. For larger plants, follow the same techniques as for trees and shrubs.
* Seeds: Plant seeds according to the instructions on the seed packet. Make sure to sow them at the correct depth and spacing.
Soil Preparation
The quality of your soil is crucial for plant growth. Proper soil preparation involves:
* Testing: Start by testing your soil to determine its pH and nutrient levels. This will help you determine what amendments are needed.
* Amendments: Add organic matter to your soil, such as compost, manure, or leaf mold, to improve drainage, aeration, and nutrient content.
* Tilling: Till the soil to a depth of 6-8 inches to break up compacted soil and allow roots to penetrate easily.
Watering Practices
Water is essential for plant growth, but too much or too little water can be harmful.
* Frequency: Water deeply and infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out slightly between waterings.
* Depth: Water deeply enough to reach the roots.
* Time of Day: Water in the early morning to minimize evaporation.
Fertilization
Fertilizer provides essential nutrients for plant growth.
* Types: Choose a fertilizer specifically designed for the type of plants you are growing.
* Frequency: Fertilize regularly according to the instructions on the fertilizer package.
Pest Control
Pests and diseases can damage your plants.
* Prevention: The best way to control pests and diseases is to prevent them in the first place. This can be done by choosing disease-resistant varieties, practicing good sanitation, and providing proper care for your plants.
* Treatment: If pests or diseases do occur, treat them promptly using organic or chemical control methods.
Climate-Smart Gardening Practices
Gardening in harmony with nature is not just about choosing the right plants; it's about embracing practices that promote sustainability and resilience in the face of changing climates. Climate-smart gardening focuses on minimizing environmental impact, conserving resources, and supporting biodiversity.
Water Conservation
Water is a precious resource, and conserving it is crucial for sustainable gardening. Different climates require different approaches to water conservation:
- Arid and Semi-Arid Climates: In these regions, water conservation is paramount. Consider using drought-tolerant native plants that require minimal watering. Implementing water-wise irrigation techniques like drip irrigation or soaker hoses can significantly reduce water waste. Mulching around plants helps retain moisture and reduce evaporation.
- Humid Climates: While rainfall is abundant in humid climates, water conservation is still important. Choose plants that thrive in moderate moisture conditions and avoid overwatering. Collecting rainwater in barrels can be a valuable source for watering plants during dry spells.
Native Plants and Ecosystem Support
Native plants are adapted to local climates and soil conditions, requiring less water and maintenance than non-native species. Their deep root systems help stabilize soil, prevent erosion, and filter pollutants. Native plants also provide food and shelter for local wildlife, contributing to biodiversity and ecosystem health.
- Examples of Native Plants: Choosing native plants is a key step towards climate-smart gardening. For instance, in the United States, the National Audubon Society offers a comprehensive list of native plants for various regions, including recommendations for attracting pollinators.
- Benefits of Native Plants: Native plants are often more resilient to pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. They also contribute to the natural beauty of the landscape, creating a sense of place and connection to the local environment.
Sustainable Gardening Practices, Choosing the right plants for your climate
Beyond water conservation and native plants, there are numerous sustainable practices that promote biodiversity and reduce environmental impact:
- Composting: Composting organic waste from the garden and kitchen reduces landfill waste and provides a rich source of nutrients for plants. It improves soil structure, reduces the need for chemical fertilizers, and enhances soil fertility.
- Organic Pest Control: Using natural pest control methods like beneficial insects, companion planting, and organic pesticides minimizes chemical exposure and protects beneficial organisms in the garden.
- No-Till Gardening: This practice minimizes soil disturbance, preserving soil structure and beneficial microorganisms. It reduces erosion, improves water infiltration, and enhances soil health.
Resources and Organizations
Numerous organizations and resources offer support and information on climate-smart gardening practices:
- The National Wildlife Federation: This organization provides comprehensive resources on gardening for wildlife, including tips on creating pollinator gardens and attracting birds.
- The Xerces Society for Invertebrate Conservation: This organization focuses on protecting pollinators and offers guidance on creating pollinator-friendly gardens.
- The Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center: This center provides resources on native plants and sustainable gardening practices, with a focus on promoting biodiversity.
Popular Questions
Choosing the right plants for your climate - What if my climate is unpredictable?
Choose plants known for their adaptability and resilience. Look for varieties that can tolerate fluctuations in temperature, rainfall, and sunlight. Consult with local nurseries for recommendations based on your specific microclimate.
How can I determine the best planting time for my region?
Check your local gardening calendar or consult with a local nursery. Planting times vary depending on the specific plant and the climate zone. Generally, it's best to plant during the cooler months when the soil is moist and temperatures are moderate.
Are there any resources for learning more about climate-smart gardening?
Yes! Many organizations offer valuable information and resources. Check with your local extension office, botanical gardens, and environmental groups. Online platforms and gardening magazines also provide valuable insights and tips.
